Based on Graphene/Molybdenum Disulfide Composite

The Graphene/Molybdenum Disulfide Composite is an advanced compound that has gained attention in recent years as an additive in lubricants. This composite is composed of graphene and molybdenum disulfide. Each of these materials individually shows outstanding anti-wear and anti-friction properties. Combining these two materials creates an exceptionally powerful additive designed to improve the performance of lubricants in high-temperature conditions, heavy pressures, and corrosive environments. The benefits of using this additive include: significant reduction in friction, exceptional thermal tolerance, resistance to extreme pressures, increased lifespan of components, outstanding chemical stability and corrosion resistance, high electrical and thermal conductivity.
Applications of oil additive based on graphene/molybdenum disulfide composite
Aerospace Industry:
- In the aerospace sector, where equipment operates under extremely high temperatures and pressures, the graphene/molybdenum disulfide composite is used as an additive in lubricating oils to improve performance and extend the lifespan of components. This composite finds applications in jet engines, turbines, and hydraulic systems.
Automotive Industry:
- In internal combustion engines and automotive gearboxes, the Graphene/Molybdenum Disulfide Composite helps reduce friction and wear, resulting in lower fuel consumption and increased efficiency. Additionally, this composite enhances performance under harsh driving conditions, such as high pressures and extreme temperatures.
Heavy Industrial Machinery:
- In mining, agricultural, and construction equipment that operates under heavy loads and high temperatures, lubricants containing Graphene/Molybdenum Disulfide help reduce wear and extend the lifespan of components. This composite minimizes premature failures and enhances overall efficiency.
Military and Marine Industries:
In military equipment and underwater systems, this composite is highly effective due to its corrosion resistance and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Lubricants infused with this composite improve equipment performance and extend their service life.



Pin On Disk Wear Test
In the Pin on Disk Wear test, the coefficient of friction is examined. For this purpose, Two samples were tested according to ASTM G99 standards; a base oil and a base oil mixed with 0.4% Wt additive based on Graphene/Molybdenum Disulfide composite (G/MoS2) additive.

The test was conducted at a temperature of 100 ºC according to ASTM G99 standards. The applied force was 200 Newtons, the sliding distance was 1000 meters, and the motor speed was 250 rpm.
In this test, it was observed that the coefficient of friction for the base oil mixture with 0.4% Wt by G/MoS2 was lower than that of the base oil. This reduction in the coefficient of friction shows that the addition of MoS2 nanoparticles to the base oil reduces friction. These nanoparticles form a thin layer between moving surfaces, minimizing direct contact and preventing wear. Also, graphene, as a high-strength nanomaterial with excellent thermal stability, performs effectively under high-temperature conditions. This property makes lubricants containing this composite highly effective in harsh operating environments. The tests indicate that lubricating oils based on G/MoS2 show significantly lower coefficients of friction compared to pure base oils.
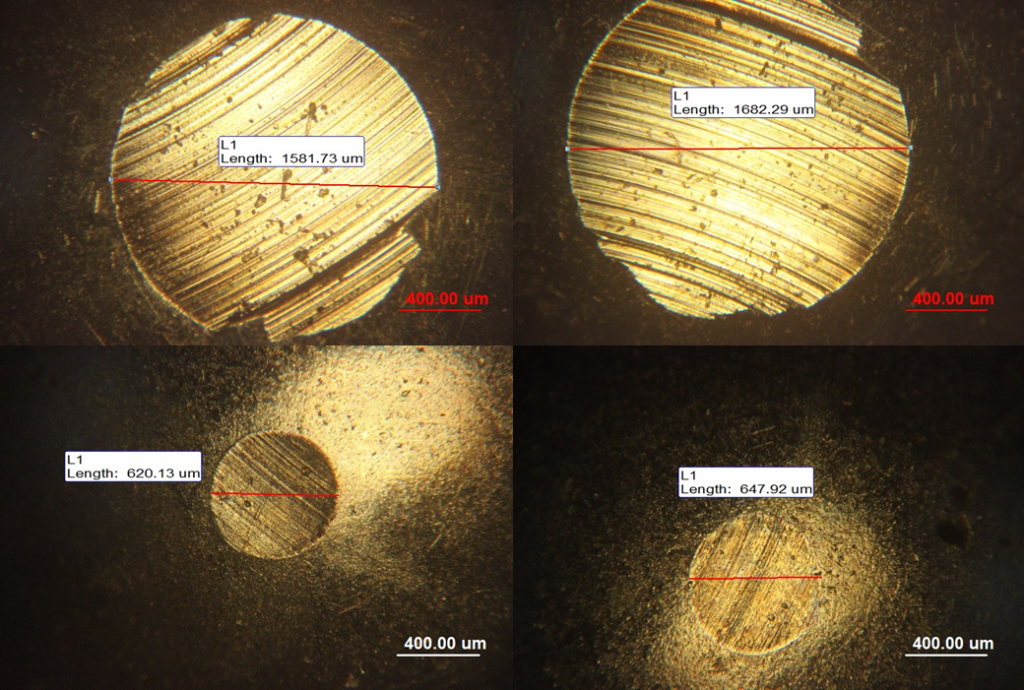
Images of the four-ball test: The test was conducted with an applied force of 392 Newtons, over a time of 3600 seconds, with a motor speed of 1200 rpm.
Wear Test (Four-ball Test)
The four-ball test or wear test is another test that can determine the effect of various additives in oil on the amount of wear. Below are the images of this test to compare the wear level when using base oil and base oil mixed with graphene/molybdenum disulfide composite (G/MoS2) additive.
In the four-ball test, images (a) and (b) represent the base oil without the G/MoS2 composite-based additive. They show wear track lengths of 1581.73 μm and 1682.29 μm, respectively. Images (c) and (d) pertain to the base oil correspond to the G/MoS2 composite-based additive, which show wear track lengths of 647.92 μm and 623.13 μm, respectively.
In general, these images show that when using base oil, the surfaces are exposed to direct wear, and the effects of wear are clearly visible. The wear tracks are long and extensive.
This shows a greater damaged surface. But when graphene/molybdenum disulfide composite (G/MoS2)-based additive are added to the base oil, they effectively reduce length of the wear track.
This indicates superior performance of MoS2 nanoparticles and graphene in reducing wear and friction. The MoS2 nanoparticles act as a protective layer and reduce the direct contact between surfaces. Graphene, as a robust and stable material, improves the lubrication properties. The results from these images clearly show that adding MoS2 and graphene nanoparticles to base oil can lead to a significant reduction in surface wear. The comparison of wear track lengths shows that oils containing these nanoparticles can perform much better under operational conditions.
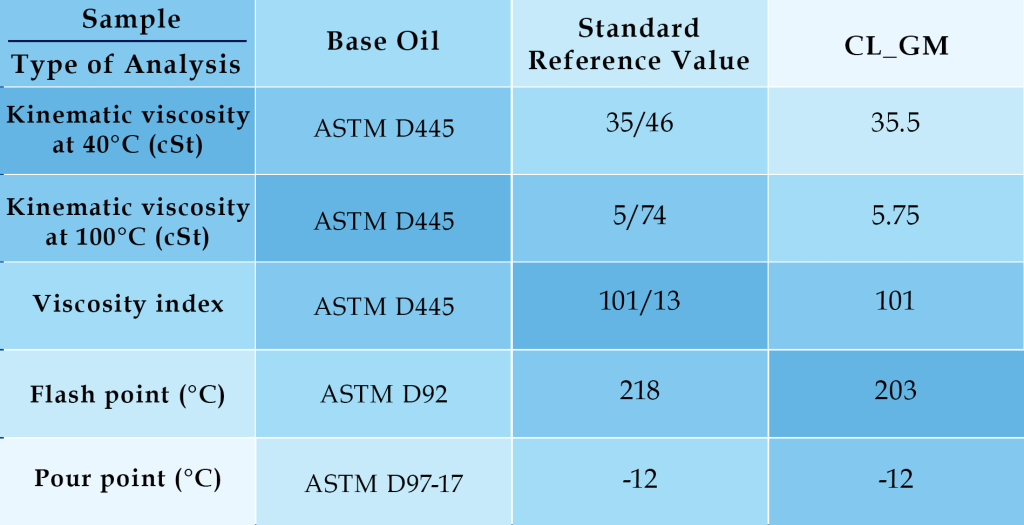
Table: Oil Additive Based on Graphene/Molybdenum Disulfide Composite (G/MoS2)